Page Not Found
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
The BI lab
This is a page not in th emain menu
The TX-APCD includes medical, pharmacy, and dental claims, as well as eligibility and provider files, collected from private and public payors. It will contain administrative claims information on approximately 60% of all covered Texans, representing nearly 100% of medical claims regulated by the state.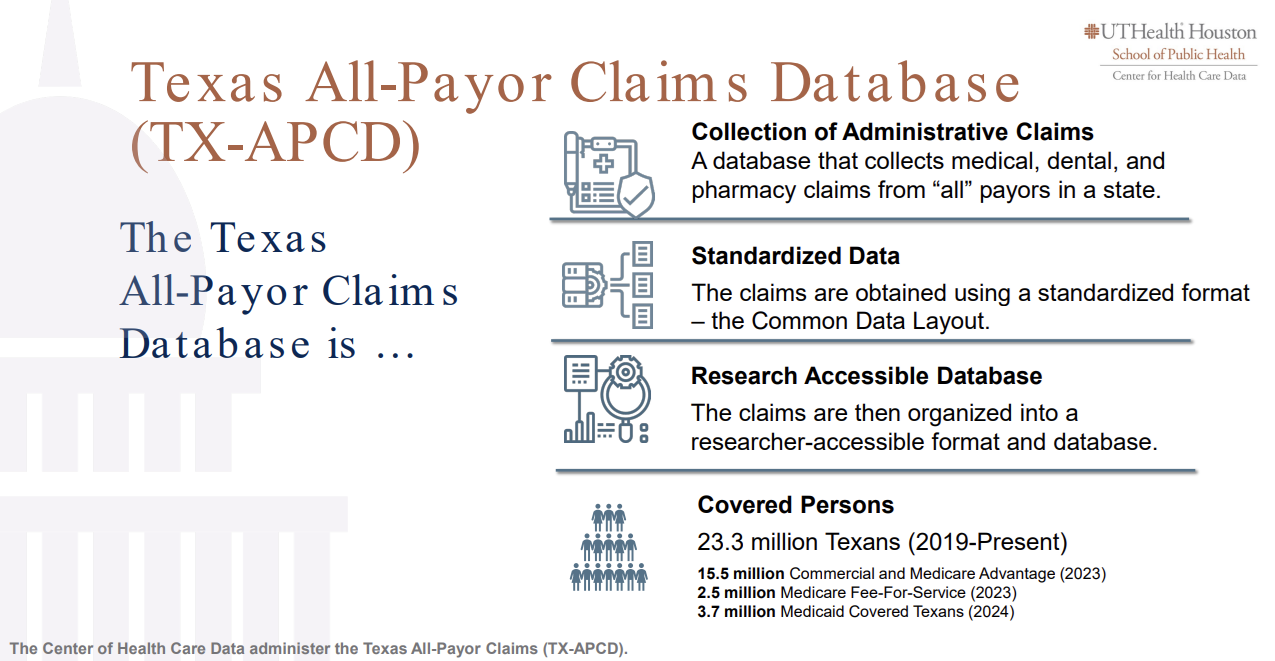
The TX-APCD includes medical, pharmacy, and dental claims, as well as eligibility and provider files, collected from private and public payors. It will contain administrative claims information on approximately 60% of all covered Texans, representing nearly 100% of medical claims regulated by the state.
Insight Net is a national network of centers working to improve our collective ability to understand, predict, prepare for, and respond to infectious disease threats through collaboration between analytic experts and public health departments..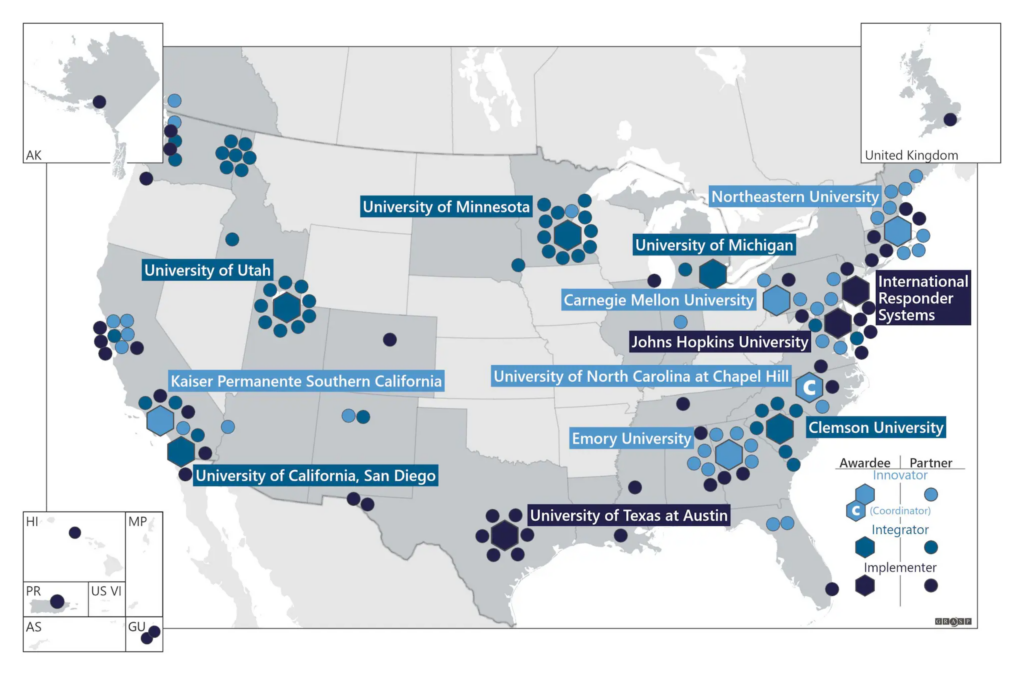
The SMH pathogen-specific projections provide real-time modeling evidence aiming to support ongoing public health needs. SMH currently produces projections for COVID-19, seasonal influenza, and Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), each addressing different public health questions and uncertainties.
Published:
This post will show up by default. To disable scheduling of future posts, edit config.yml and set future: false.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
We are developing a digital twin model that integrates multiple data sources to enhance public health decision-making in Texas. This tool will be applied to the long-term study of respiratory diseases, sexually transmitted diseases, vector-borne diseases, opioid transmission, and chronic diseases.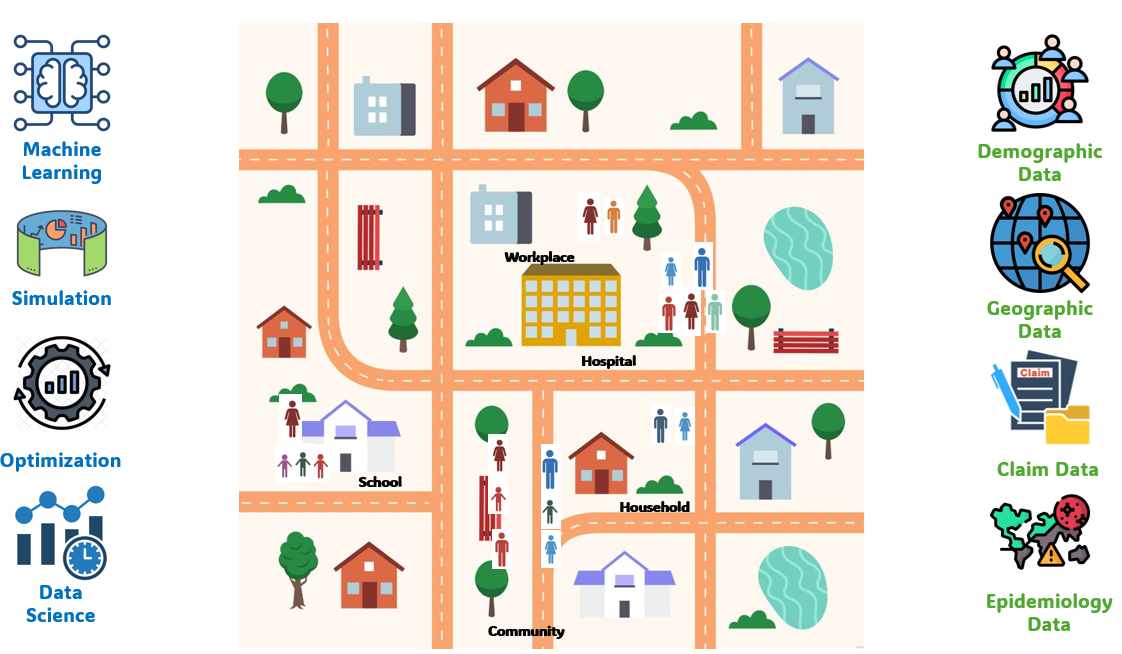
We are training neural networks to augment epidemiological models by improving parameter estimation, identifying abnormal trends, and enhancing the models’ data-driven capabilities.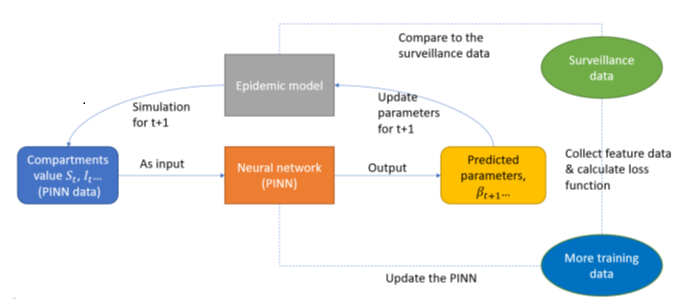
We are conducting infectious disease model simulations using what-if scenarios for COVID-19, Influenza, and RSV at national, state, and city levels to support public health agencies in epidemic preparedness and evaluating the impact of interventions. 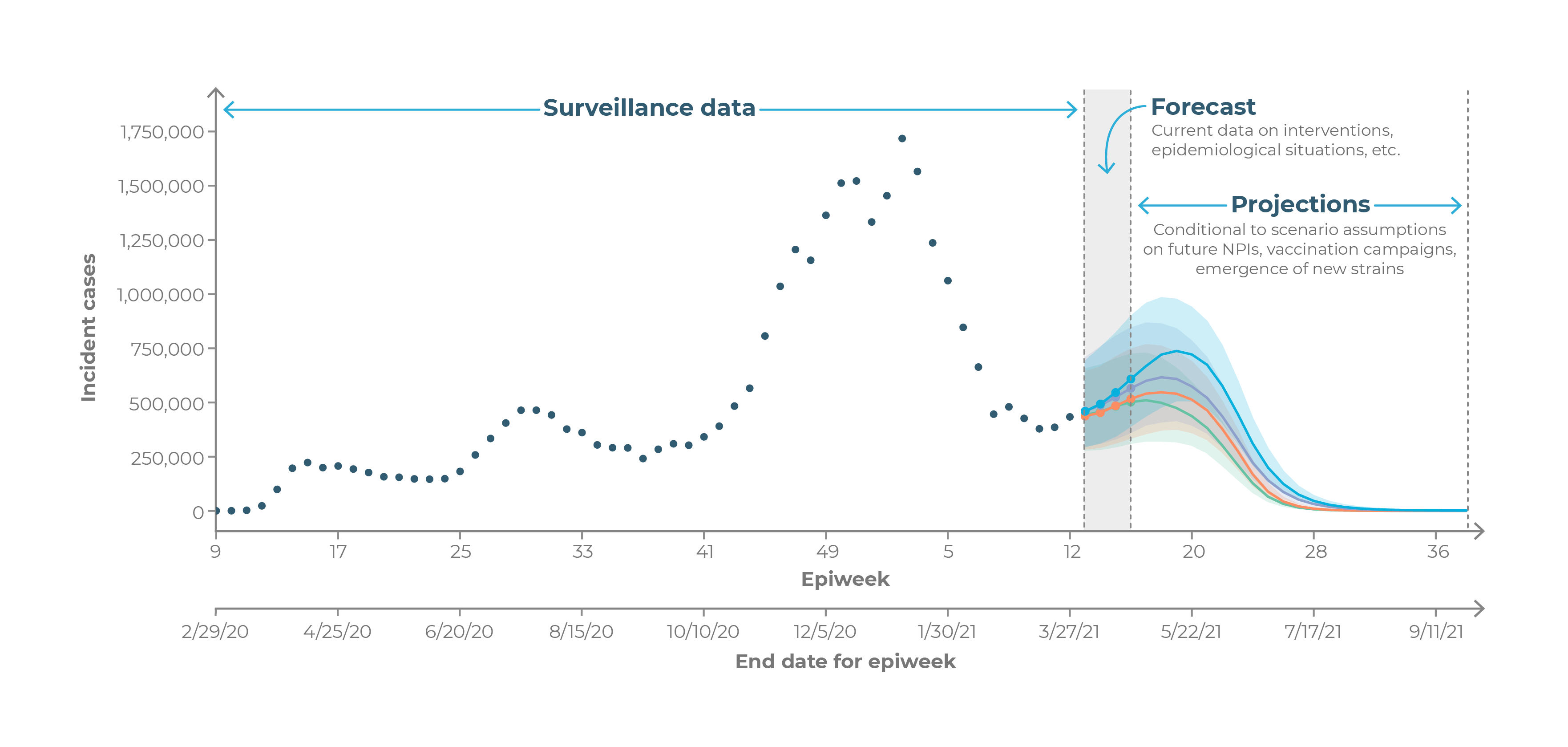
We are employing diverse optimization techniques to address the optimal control problem and reduce overall epidemic costs—encompassing both infection-related and intervention expenses. Our approach integrates rigorous theoretical methodologies with data-driven strategies. 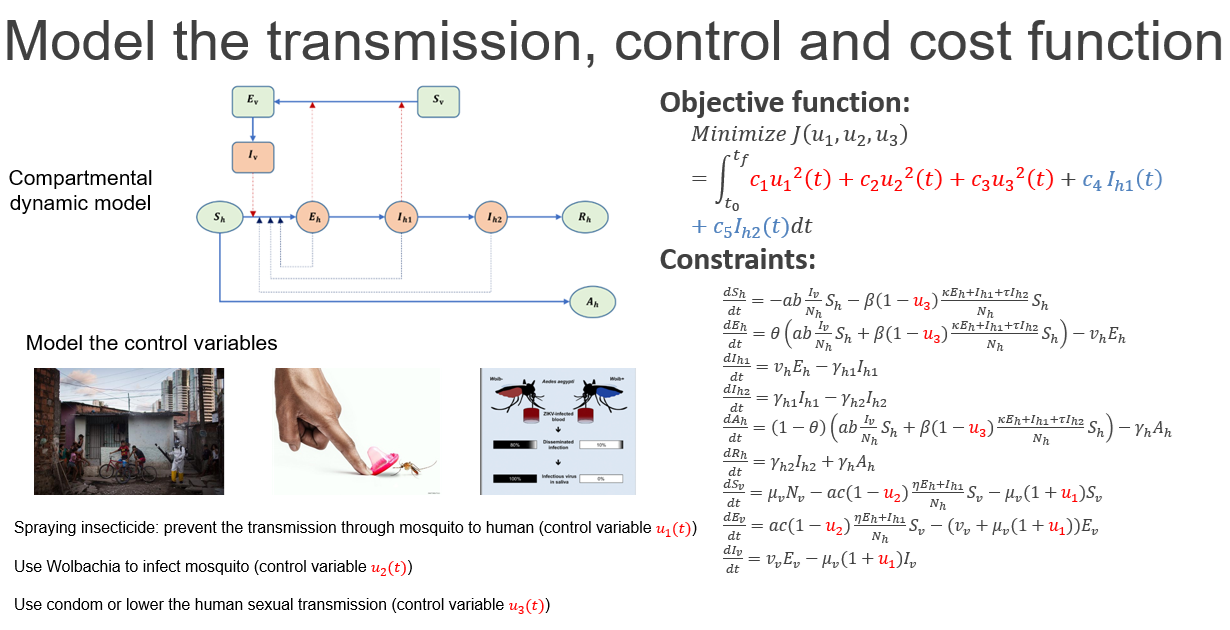
Published in Journal of mathematical biology, 2016
Recommended citation: Zhao, Songnian, Yan Kuang, Chih-Hang Wu, David Ben-Arieh, Marcelo Ramalho-Ortigao, and Kaiming Bi. "Zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis transmission: modeling, backward bifurcation, and optimal control." Journal of mathematical biology 73, no. 6-7 (2016): 1525-1560.
Published in Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2017
Recommended citation: Chen, Yuyang, Kaiming Bi, Songnian Zhao, David Ben-Arieh, and Chih-Hang John Wu. "Modeling individual fear factor with optimal control in a disease-dynamic system." Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 104 (2017): 531-545.
Published in IISE Transactions on Healthcare Systems Engineering, 2018
Recommended citation: Zhao, Songnian, Yan Kuang, Chih-Hang Wu, Kaiming Bi, and David Ben-Arieh. "Risk perception and human behaviors in epidemics." IISE Transactions on Healthcare Systems Engineering 8, no. 4 (2018): 315-328.
Published in BioMed research international, 2018
Recommended citation: Bi, Kaiming, Yuyang Chen, Songnian Zhao, Yan Kuang, and Chih-Hang John Wu. "Current visceral leishmaniasis research: a research review to inspire future study." BioMed research international 2018 (2018).
Published in Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2019
Recommended citation: Bi, Kaiming, Yuyang Chen, Songnian Zhao, David Ben-Arieh, and Chih-Hang John Wu. "Modeling learning and forgetting processes with the corresponding impacts on human behaviors in infectious disease epidemics." Computers & Industrial Engineering 129 (2019): 563-577.
Published in Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2019
Recommended citation: Chen, Yuyang, Kaiming Bi, Chih-Hang John Wu, and David Ben-Arieh. "A new evidence-based optimal control in healthcare delivery: A better clinical treatment management for septic patients." Computers & Industrial Engineering 137 (2019): 106010.
Published in Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2020
Recommended citation: Bi, Kaiming, Yuyang Chen, Chih-Hang John Wu, and David Ben-Arieh. "A Memetic Algorithm for Solving Optimal Control Problems of Zika Virus Epidemic with Equilibriums and Backward Bifurcation Analysis." Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation (2020): 105176.
Published in Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2020
Recommended citation: Bi, Kaiming, Yuyang Chen, Songnian Zhao, David Ben-Arieh, and Chih-Hang John Wu. "A new zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis dynamic transmission model with age-structure." Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 133 (2020): 109622.
Published in Progress in Additive Manufacturing, 2021
Recommended citation: Bi, Kaiming, Dong Lin, Yiliang Liao, Chih-Hang Wu, and Pedram Parandoush. "Additive manufacturing embraces big data." Progress in Additive Manufacturing (2021): 1-17.
Published in Arxiv, 2021
Recommended citation: Chen, Yuyang, Kaiming Bi, Chih-Hang J. Wu, David Ben-Arieh, and Ashesh Sinha. "A New Bayesian Optimization Algorithm for Complex High-Dimensional Disease Epidemic Systems." arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.00062 (2021).
Published in Arxiv, 2021
Recommended citation: Chen, Yuyang, Kaiming Bi, Chih-Hang J. Wu, David Ben-Arieh, and Ashesh Sinha. "A New Bayesian Optimization Algorithm for Complex High-Dimensional Disease Epidemic Systems." arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.02289 (2021).
Published in Arxiv, 2022
Recommended citation: Chen, Yuyang, Kaiming Bi, Chih-Hang J. Wu, David Ben-Arieh, and Ashesh Sinha. "An Improved Mathematical Model of Sepsis: Modeling, Bifurcation Analysis, and Optimal Control Study for Complex Nonlinear Infectious Disease System." arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.02702 (2022).
Published in Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2022
Recommended citation: Bi, Kaiming, Yuyang Chen, Chih-Hang John Wu, and David Ben-Arieh. "Learning-based impulse control with event-triggered conditions for an epidemic dynamic system." Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation 108 (2022): 106204.
Published in UT Austin Report, 2022
Recommended citation: Bi, Kaiming, Anass Bouchnita, Oluwaseun F. Egbelowo, Spencer Fox, Michael Lachmann, and Lauren Ancel Meyers. "Scenario projections for the spread of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA. 4 and BA. 5 subvariants in the US and Texas." (2022).
Published in Epidemics, 2023
Recommended citation: Bi, Kaiming, Jose Luis Herrera-Diestra, Yuan Bai, Zhanwei Du, Lin Wang, Graham Gibson, Maureen Johnson-Leon, Spencer J. Fox, and Lauren Ancel Meyers. "The risk of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant emergence in low and middle-income countries (LMICs)." Epidemics 42 (2023): 100660.
Published in The European Physical Journal Plus, 2023
Recommended citation: Bandekar, Shraddha Ramdas, Mini Ghosh, and Kaiming Bi. "Impact of high-risk and low-risk population on COVID-19 dynamics considering antimicrobial resistance and control strategies." The European Physical Journal Plus 138, no. 8 (2023): 697.
Published in Researchsquare, 2023
Recommended citation: Meyers, Lauren, Kaiming Bi, Shraddha Bandekar, Anass Bouchnita, and Spencer Fox. "Scenario Projections for SARS-CoV-2, Influenza, and RSV Burden in the US (2023-2024)." (2023).
Published in Nature communications, 2023
Recommended citation: Howerton, Emily, Lucie Contamin, Luke C. Mullany, Michelle Qin, Nicholas G. Reich, Samantha Bents, Rebecca K. Borchering et al. "Evaluation of the US COVID-19 Scenario Modeling Hub for informing pandemic response under uncertainty." Nature communications 14, no. 1 (2023): 7260.
Published in Epidemics, 2024
Recommended citation: Bouchnita, Anass, Kaiming Bi, Spencer J. Fox, and Lauren Ancel Meyers. "Projecting Omicron scenarios in the US while tracking population-level immunity." Epidemics 46 (2024): 100746.
Published in PLoS medicine, 2024
Recommended citation: Jung, Sung-mok, Sara L. Loo, Emily Howerton, Lucie Contamin, Claire P. Smith, Erica C. Carcelén, Katie Yan et al. "Potential impact of annual vaccination with reformulated COVID-19 vaccines: Lessons from the US COVID-19 scenario modeling hub." PLoS medicine 21, no. 4 (2024): e1004387.
Published in SSRN, 2025
Recommended citation: Chen, Ruohan, Zengyang Shao, Kaiming Bi, Benjamin J. Cowling, and Zhanwei Du. "Evaluating the Health Economic Impacts of Baloxavir Marboxil and Oseltamivir for the Treatment of Influenza in Adult Outpatients in Hong Kong: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis." Available at SSRN 5085546.
Published in Mathematical Modelling of Natural Phenomena, 2025
Recommended citation: Bouchnita Anass, Bandekar Shraddha, Bi Kaiming et al. "The interplay between evolutionary and immunological dynamics regulates virus variant emergence and competition." Mathematical Modelling of Natural Phenomena, no. 6 (2025)
Published in Emerging infectious diseases, 2025
Recommended citation: Kaiming B, Bandekar SR, Bouchnita A, Fox SJ, Ancel Meyers L. Annual hospitalizations for COVID-19, influenza, and respiratory syncytial virus, United States, 2023–2024. Emerg Infect Dis. 2025 Mar [date cited]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid3103.240594
TEPHI is a network of public health professionals and resources that will ensure the state is at the forefront of pandemic readiness and response to keep Texans safe and the economy strong.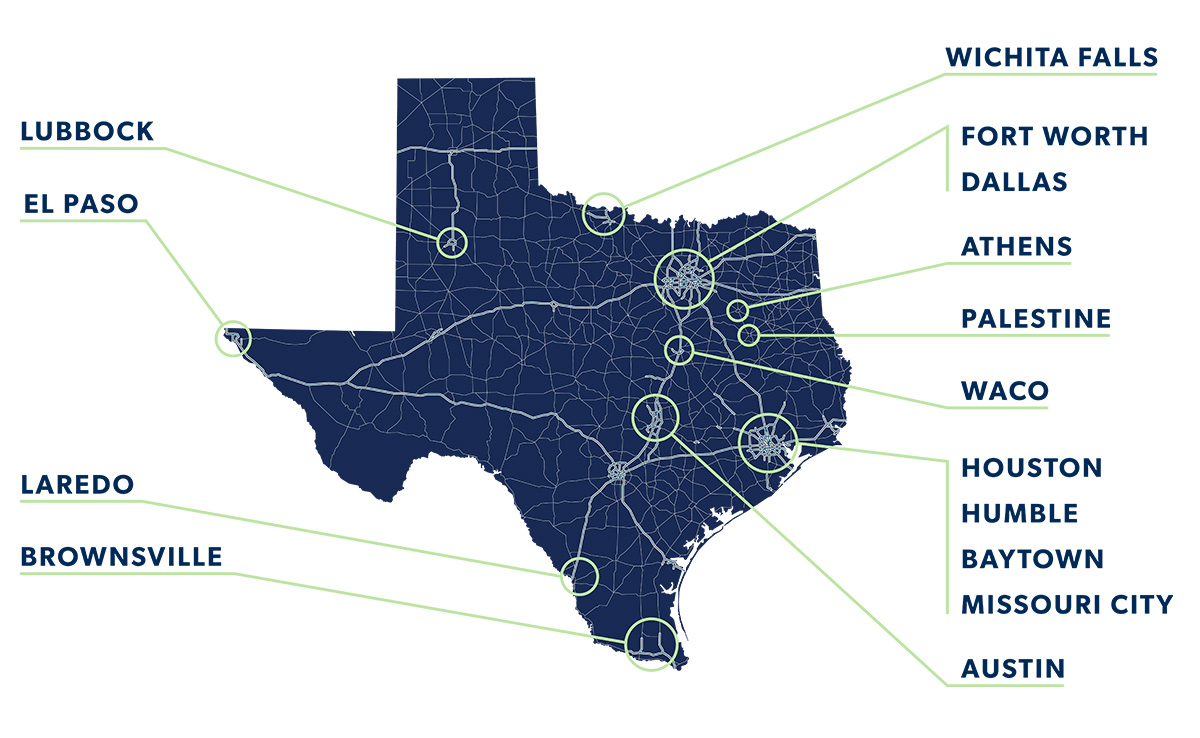
The TX-APCD includes medical, pharmacy, and dental claims, as well as eligibility and provider files, collected from private and public payors. It will contain administrative claims information on approximately 60% of all covered Texans, representing nearly 100% of medical claims regulated by the state.
Insight Net is a national network of centers working to improve our collective ability to understand, predict, prepare for, and respond to infectious disease threats through collaboration between analytic experts and public health departments..
The SMH pathogen-specific projections provide real-time modeling evidence aiming to support ongoing public health needs. SMH currently produces projections for COVID-19, seasonal influenza, and Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), each addressing different public health questions and uncertainties.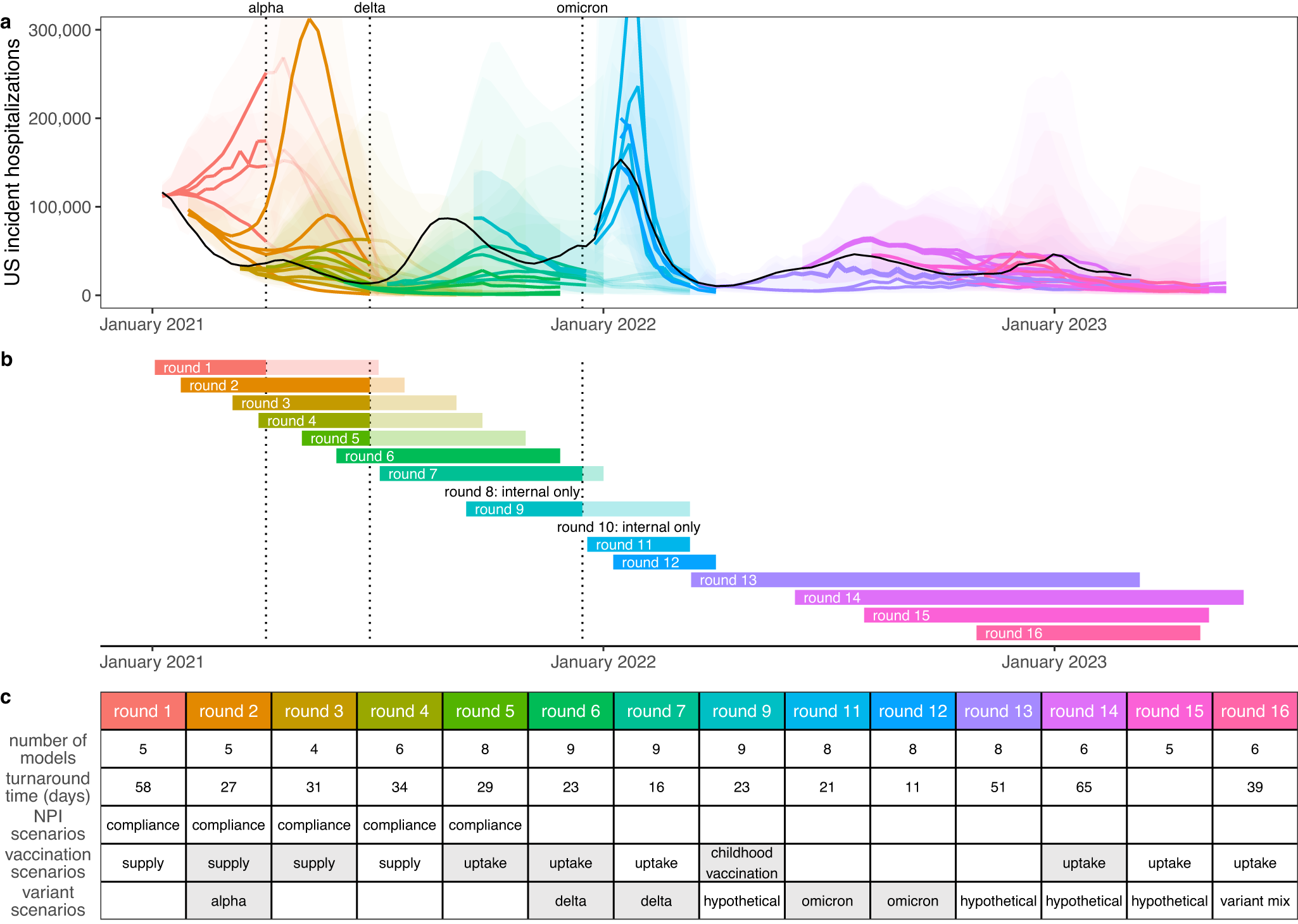
Graduate Course, Kansas State University, IMSE Department, 2015
Working as a graduate teaching assistant, Grade Homework and Hold help sessions
Undergraduate Course, Kansas State University, IMSE Department, 2016
Working as a graduate teaching assistant, Grade Homework and Hold help sessions
Undergraduate Course, Kansas State University, IMSE Department, 2018
Working as an instructor, teach simulation software, meet 50 students once a week
PhD Course, UT Health, School of Public Health, 2025
Instructor, teaching PhD level students how to use modeling and simulation to evaluate health policy in infectious diseases.